Windows Grep is a free search tool for Windows that allows you search the text of multiple files at the same time.
Its interface, although simple, is very practical and, thanks to its assistant, it is really easy to perform searches.
You can make various adjustments to ensure you find the file that you want, such as the use of regular expressions or identical terms, the ability to search multiple directories, or eliminate files by extension, among other options.
All this makes Windows Grep a utility that is really worth trying.
One of the first Linux commands that many system administrators learn is grep. This venerable tool has been around for decades and is crucial to any administrator’s toolbelt. Grep’s core is simply the ability to search plain text for a RegEx pattern. Grep can search files in a given directory or streamed input to output matches. Did you know PowerShell has grep? Well.almost.
Do you want to start taking your PowerShell scripting more seriously? Takamine c132s serial number. Learn how to easily build PowerShell GUIs, protect your scripts and enhance the PowerShell experience in Visual Studio with Adam Driscoll’s PowerShell Pro Tools!
The grep command provides access to the grep utility, a powerful file processing tool used to find patterns in text files. It has many practical use cases and is certainly one of the most used Linux commands. This guide illustrates some simple yet useful Linux grep commands that have real-world uses. Example File for Demonstration.
Cached
- Apr 07, 2017 by Scott Matteson in Open Source on April 7, 2017, 8:27 AM PST The grep command is a powerful tool for searching for files or information. Learn some strategies for using it effectively.
- Another grep tool I now use all the time on Windows is AstroGrep: Its ability to show me more than just the line search (i.e. The -context=NUM of a command-line grep) is invaluable. Very fast, even on an old computer with non- SSD drive (I know, they used to do this hard drive with spinning disks, called platters, crazy right?).
PowerShell, being a language, is more than just a single purpose binary. Therefore what built-in abilities exist to search for plain text using RegEx patterns much like grep does? In this article we explore the myriad ways to search for text in files using PowerShell.
Exploring the Select-String Cmdlet
Select-String (our PowerShell grep) works on lines of text and by default will looks for the first match in each line and then displays the file name, line number, and the text within the matched line. Additionally, Select-String can work with different file encodings, such as Unicode text, by use the byte-order-mark (BOM) to determine the encoding format. If the BOM is missing, Select-String will assume it is a UTF8 file.
Parameters of Select-String
AllMatches– Normally,Select-Stringwill only look for the first match in each line, using this parameter the cmdlet will search for more than one match. A singleMatchInfoobject will still be emitted for each line, but it will contain all of the matches found.CaseSensitive– Matches are not case-sensitive by default, this forces the cmdlet to look for matches that match exactly to the input pattern.Context– A very useful parameter in that, you can define the number of lines before and after the match that will be displayed. Adding this parameter modifies the emittedMatchInfoobject to include a newContextproperty that contains the lines specified.
Grep Tool For Mac
Keep in mind that if you pipe the output of Select-String to another Select-String call, the context won’t be available since you are only searching on the single resulting MatchInfoline property.
Culture– Used with theSimpleMatchparameter, this specifies a culture to be matched with the specified pattern. This includes options such asen-US,es, orfr-FRas examples. A few other useful options is theOrdinalandInvariantoptions.Ordinalis for non-linguistic binary comparisons andInvariantis for culture independent comparisons.
This parameter was introduced in PowerShell 7 and is not available to prior versions. Also keep in mind that this will use the current culture of the system, by default, which can be found using Get-Culture.
Encoding– Specify the encoding of the target file to search, which a default ofutf8NoBOM.ascii: Uses the encoding for the ASCII (7-bit) character set.bigendianunicode: Encodes in UTF-16 format using the big-endian byte order.oem: Uses the default encoding for MS-DOS and console programs.unicode: Encodes in UTF-16 format using the little-endian byte order.utf7: Encodes in UTF-7 format.utf8: Encodes in UTF-8 format.utf8BOM: Encodes in UTF-8 format with Byte Order Mark (BOM)utf8NoBOM: Encodes in UTF-8 format without Byte Order Mark (BOM)utf32: Encodes in UTF-32 format.
Encodingparameter also accepts numeric IDs of registered code pages such as1251or string names such aswindows-1251.
Starting with PowerShell Core 6.2, the Encoding parameter also accepts numeric IDs of registered code pages such as 1251 or string names such as windows-1251.
Exclude– Working with thePathparameter, exclude specific items using a pattern, such as*.txt.Include– Just like theExcludeparameter,Includewill include only the specified items using a pattern, such as*.log.List– Only return the first instance of matching text from each input file. This is intended to be a fast and efficient way to retrieve a listing of files that have matching contents.LiteralPath– This tellsSelect-Stringto use the values as input, instead of interpreting values such as*as a wildcard. If the path includes escape characters, enclose them in single quotation marks to do no interpretation.NoEmphasis– Instead of highlighting the string that the pattern is matched upon, disable the highlighting of matches. By default, emphasis uses negative colors based on the background text colors.NotMatch– Look for text that does not match the specified pattern.Path– Specify the path to the files to search. Wildcards are permitted, but you cannot specify only a directory. The default is the local directory.Pattern– The pattern to search the input content or files for based on RegEx.SimpleMatch– Use a simple match instead of regular expressions. Since RegEx is not used, the returnedMatchInfoobject does not have any values in theMatchesproperty.Raw– Output the matching strings, without aMatchInfoobject. This is the behavior that is most similar togrepand not the more object oriented nature of PowerShell.Quiet– Only return a$trueor$falseif the pattern is found.
Using PowerShell Grep err… Select-String
Of course knowing how the parameters and options of a cmdlet work is not quite the same as using it in a production environment. Let’s dive into examples and see how we can leverage Select-String to make find text matches easier.

There are three ways that we can use Select-String to find matches.
- Pipe in quoted text to the
Select-Stringcmdlet, i.e. stream in the text. - Using text stored in a variable, pass the variable to the
InputObjectparameter. - Use the
Pathparameter to specify files to search for the text in.
The files we are using for testing this are randomly generated content, but of the same type as often found in production systems.
Simple Matching in Files
Starting off with a very simple example, let us look for Joe in a handful of CSV files.
As you can tell, this is pretty simple, we see how Joe is highlighted on the line with the rest of the data. But what data is actually being returned here? Let us take a look at all of the properties of a returned match.
Grep Tool Windows 10
We have a couple of properties here that are useful. Notably the line, path, pattern, and matches. Most of what we want to know is in the matches property.
Here you can see how even though we used a simple expression, this is still a RegEx expression and the subsequent details available.
What if we look for several different values using comma separated patterns? This is useful as this actually defines three different patterns and not one complex RegEx value.
GREP Gen - Regex Tester/Debugger
You can see how this is the case, if we select only the filename, pattern, and line from our search.
More Complex RegEx Matching
Now that we demonstrated some of the simpler matching methods, what about utilizing RegEx more to actually look for more useful patterns? The three examples here are looking for Email Addresses, IP Addresses, and Social Security Numbers (SSNs). The patterns used here are not the only way to construct a RegEx search, and there may be easier ways. PowerShell Grep (Select-String) is a pretty advanced cmdlet.
Let’s look to see if emails are contained in our files. Using a somewhat complex RegEx match, as shown below, will demonstrate finding those matches.
Of course, of more concern might be if there were SSNs included in a file. A very simple match for this would be the following.
Finally, what if we wanted to look up some IP Addresses in our file? Using another RegEx expression to look for that pattern, makes quick work.
A caveat about this RegEx. Technically, this will match values up to 999.999.999.999 which is an invalid IP. You can construct more accurate RegEx expressions that will get longer, but it is a trade off depending on what you are looking to do.
Searching with Context
Context is very useful in troubleshooting, it helps to explain what is happening prior to an event occurring and after. For example, let’s search in an Apache log and find this suspendedpage.cgi text.
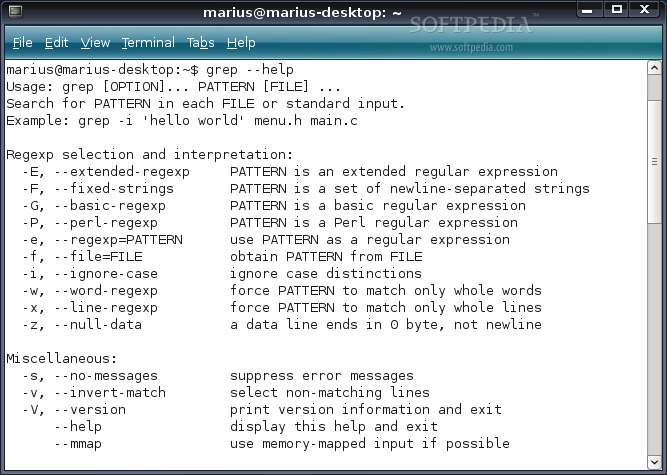
The > simple indicates the matched line, and there is one line prior to the match and after the match. In this example, this could tell us that the Google bot was looking for robots.txt and unfortunately received a suspendedpage.cgi result instead. Next, it went to try the homepage and perhaps got the same error.
What exactly is contained in the context property then as emitted by the MatchInfo object? If we expand upon that property, you can see that there is PreContent and PostContent. This means you can manipulate this further down the line if necessary.
Other examples of searching through log files are in articles such as Making Sense of the Microsoft DNS Debug Log which demonstrates using Select-String to look through a DNS debug log. The PowerShell grep is strong in that post.
Conclusion
Grep is an incredibly useful tool in the Linux world, and Select-String offers much of the same functionality in the PowerShell world. Adding in the object-oriented nature of PowerShell only serves to enhance the utility and usefulness that the cmdlet offers.
For many System Administrators, being able to quickly and efficiently search log files over varying types, along with understanding context, is an incredibly important and necessary ability. PowerShell Select-String makes this easy to do and saves countless hours of troubleshooting!
More from Adam The Automator & Friends